 |
Bangalore, India (SPX) Dec 29, 2008 The moon mineralogy mapper (M3), a scientific instrument of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) onboard India's first lunar mission Chandrayaan-1, found iron-bearing minerals on the lunar surface, the US space agency said Thursday. "The mapper spectrometer has beamed images of the Orientale Basin region of the moon, indicating abundance of iron-bearing minerals such as pyroxene. Using different wavelengths of light, the instrument has also revealed for the first time changes in rock and mineral composition," M3 principal investigator Carle Pieters said in a statement hosted on NASA website. Data from the 7-kg mapper provides space scientists first opportunity to examine lunar mineralogy at high spatial and spectral resolution. The Orientale Basin is located on the moon's western limb. M3 captured the data last week when Chandrayaan was orbiting the moon at an altitude of 100 km. "The imaging spectrometer provides us with compositional information across the moon that we have never had access to before. Our ability to identify and map the composition of the surface in geologic context provides a new level of detail needed to explore and understand the earth's nearest celestial neighbour," affirmed Pieters, who teaches at Brown University in Rhode Island. The mapper was selected as a mission of opportunity through the NASA discovery programme. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory designed and built the instrument at Pasadena in California. "M3 will also help in characterising and mapping lunar minerals for knowing the moon's early geological evolution. Its compositional maps will improve our understanding of the early evolution of a differentiated planetary body and provide a high-resolution assessment of lunar resources," Chandrayaan project director M. Annadurai averred. M3 is one of the 10 instruments onboard the unmanned Chandrayaan, conducting experiments while the spacecraft orbits over the moon next two years. Five instruments were indigenously built by the state-run Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), while the remaining six payloads are of foreign origin, including three from the European Space Agency, two from NASA and one from Bulgaria. Chandrayaan was blasted off Oct 22 onboard the 316-tonne polar satellite launch vehicle (PSLV-C11) from ISRO's Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota spaceport, about 80 km north of Chennai. After traversing 384,000 km through the deep space for 18 days, the spacecraft entered the lunar orbit Nov 8 and its moon impact probe was lowered on the moon's surface Nov 14. Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links - Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com Lunar Dreams and more
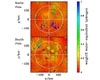 Durham, UK (SPX) Dec 23, 2008
Durham, UK (SPX) Dec 23, 2008Scientists have discovered where they believe would be the best place to find ice on the moon. Astrophysicists, led by an expert at Durham University, say if frozen water exists then it is most likely to be found near to the moon's poles in craters that are permanently shaded from the sun. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2007 - SpaceDaily.AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |