 |
Washington (AFP) May 21, 2009 NASA on Thursday said it was on target for a June mission to scour the Moon's surface for landing sites and water that would allow humans to work and even live on Earth's nearest neighbor. The space agency hopes to launch a dual craft in June, part of which would survey the Moon's surface from orbit while another unit ploughs into the lunar surface in search for water. "We had the original target of providing information back for being able to safely return to the Moon for exploration," said Mike Wargo, NASA's chief lunar scientist. The mission will focus on the little-known lunar poles, hoping to confirm reports of hydrogen accumulation and possible water-ice not found at the equatorial regions that where famously explored by humans in the last century. It is scheduled to lift-off, strapped to an Atlas V rocket, from Cape Canaveral, Florida on June 17. "One of the (resources) we are looking for is the potential of water ice at the lunar polar regions in these really mysterious permanently shadowed regions," said Wargo. The permanently shadowed craters, which may not have seen sunlight for one or two billion years, could hold deposits of ice at a temperature of minus 328 degrees fahrenheit (200 degrees celsius). Project manager Dan Andrews said the discovery of ice could be a crucial resource for future manned missions to the Moon, potentially providing oxygen for astronauts and oxidizer for rocket fuel. The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter - decked with instruments to measure temperature, topography, radioactivity and hydrogen levels - will circle the polar areas, producing three dimensional maps and data on 100 sites, some of which could later be used for manned landings. Another module, the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite, will hurtle towards the Moon's surface, crashing into a permanently shadowed crater. The impact, scheduled for October, will kick-up lunar debris six miles (9.6 kilometers) into the atmosphere, allowing observers to scan for signs of ice-water as the LCO craft flies through the debris. Although the event will be over in a matter of minutes, it may be visible from earth with the help of a telescope. It follows up on work carried out by the Lunar Prospector mission, which detected hydrogen on the Moon, but failed to detect water when, like this mission, it crashed onto the lunar surface. The mission, dubbed LCO/LCROSS, is the latest in a series of NASA lunar missions that have become representative of the agency's work. In 1969, the Apollo 11 mission touched down on the lunar surface, allowing Neil Armstrong to become the first human to set foot on the Moon. In 2004, then president George W. Bush vowed to return Americans to the Moon by 2020. But facing a massive budget deficit, President Barack Obama has called into question the fulfillment of that aim, with a review apparently underway that could delay the program. There are technical barriers, too. The space shuttle vehicle that could deliver astronauts to the Moon will be retired next year, with a new vehicle not expected in operation before 2015. Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links LRO at Goddard Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com Lunar Dreams and more
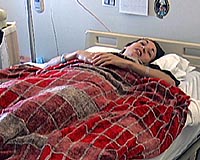 The Lunar Analog Study
The Lunar Analog StudyHouston TX (SPX) May 21, 2009 Unlike other Space Flight Simulation studies which mimic micro gravity by placing subjects in a bed with their heads inclined six degrees lower than their feet, The Lunar Analog study is a 9.5 degree head up study. Physics determines the 9.5 degrees incline - at this angle, the gravity force through the subject's legs along the long axis is 1/6th of the subject's body weight. The stu ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2009 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |