 |
Pasadena CA (SPX) Oct 12, 2009 NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has made a series of observations immediately preceding and following the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) Centaur rocket stage and shepherding spacecraft impacts at the lunar south pole, on October 9 at 7:31 and 7:35 a.m. EDT. Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) and Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) were pointed just off the southern limb of the Moon to look for a cloud of vaporized material blasted into space by the successive impacts of the rocket booster and spacecraft. The WFC3 images do not show any evidence for a temporary exosphere resulting from the impacts. Hubble's ultraviolet sensitivity allowed astronomers to look specifically for hydroxyl (OH) that would have been produced by vaporized material from the impact. The STIS and WFC3 looked for emission from OH which would have formed if water molecules had been thrown into sunlight and broken apart by ultraviolet radiation into hydrogen and hydroxyl. "A preliminary analysis of the STIS spectra do not show any clear evidence for hydroxyl, but further analysis is needed," said Hubble co-investigator Alex Storrs. The Hubble team plans on further analysis of their data. Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Hubble Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com Lunar Dreams and more
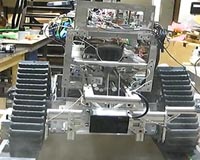 UBC Engineering Students Unveil Moon Dust-Shoveling Robot
UBC Engineering Students Unveil Moon Dust-Shoveling RobotVancouver, Canada (SPX) Oct 12, 2009 A robot designed by UBC students will be shoveling moon dust at an international robotics competition next week, vying for a $500,000 prize and the opportunity to contribute to NASA's future space exploration projects. The UBC team has created a robotic machine that can excavate simulated lunar soil (regolith). Excavating regolith will be an important part of any construction project or ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2009 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |